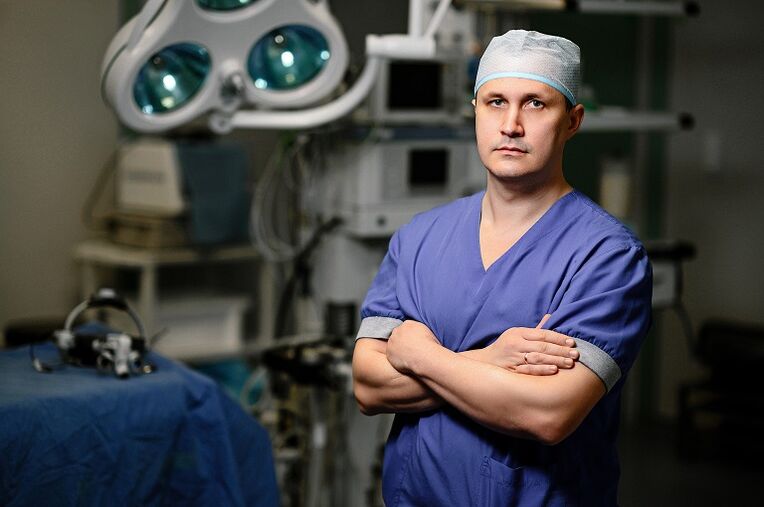
What disease is "cervical chondrosis" commonly referred to by patients? What is the correct diagnosis?
Most often, people associate this disease with pain in the cervical spine. Is this the main and/or only symptom?
Will cervical osteochondrosis cause headaches and tinnitus?
What is the cause of the pain? What options are currently available to treat such patients?
The goal is to eliminate the pain syndrome or significantly reduce its intensity and reduce the patient's need for analgesics.
Can osteochondrosis be cured?
How is the treatment strategy determined?
At what age do these problems most commonly occur?
What are the risk factors?
Is it possible to prevent it somehow?
What determines the effectiveness of treatment?
The goals of conservative treatment are to achieve a long period of remission and to minimize the frequency of exacerbations, both in duration and frequency. This also applies to acupuncture treatment methods. However, if significant changes such as hernia and spinal root compression have occurred, conservative treatment may not be effective.